GridGain Blog
The Apache Ignite native persistence storage engine follows a classic database approach based on the ARIES architecture. However, the Ignite developers needed to make some adjustments to the architecture in order to improve development speed and support memory-only storage.
In this blog, I will provide an overview of the Ignite native persistence storage engine and discuss the tradeoffs that…
The Apache Ignite community is maintained by dedicated volunteers who manage a highly informative and well-designed website. This website is regularly updated with the latest news and information about the open-source project. A section of this content, found on the GridGain blog, provides an overview of Apache Ignite's basic concepts, facts, tips, and tricks. The goal of this blog post is to…
After five days (and eleven meetings) with new customers in Europe and the Middle East, I think the time is right for another refinement of in-memory computing’s definition. To me, it is clear that our industry is lagging when it comes to explaining in-memory computing to potential customers and defining what in-memory computing is really about. We struggle to come up with a simple,…
Held on November 9, Ignite Summit Europe 2022 provided a closeup look into how Apache Ignite is being adapted for use in a variety of dynamic, demanding business settings and use cases. (Video of all sessions is available on-demand here.) Presenters were from organizations as diverse as a financial software tools, the largest food delivery company in Latin America, and the largest particle…
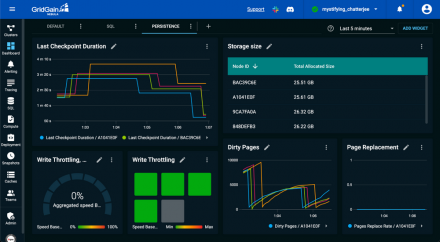
One of the most heavily used features in GridGain Nebula is the flexible dashboarding capabilities for monitoring cluster and node status. The drag-and-drop interface enables access to more than 200 metrics that are available in Apache Ignite or on the GridGain In-memory Computing Platform software running in data centers, private clouds, or the Nebula cloud.
Until now, there was no guidebook…
The Apache Ignite 3.0 Alpha 5 build recently became available. Here is an overview of the new features the community included in this release. Based on industry and use case, they may be of major interest to some developers while less relevant to others.
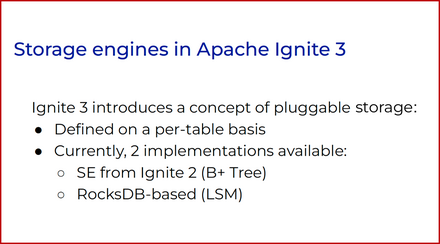
Pluggable Storage
Different use cases require different storage engines. Some storage engines are good for read-heavy operations, others…
The virtual Ignite Summit on June 14 attracted hundreds of Igniters from around the globe excited to learn and share
their experiences. (Video of all sessions is available on-demand here.)
The event, organized by GridGain and the Apache Ignite community, was preceded the day before
by free technical training sessions on Apache Ignite essentials, compute grid, and Apache Ignite with Spring Boot…
GridGain is a USA-based company that has always prided itself on being a global corporation, with employees and customers around the world. A proponent of open-source software and the original authors of the highly popular Apache Ignite in-memory platform, our company has always embraced the diversity of thought and contribution that can only come from a worldwide community.
The brutal war and…
Great news: The Apache Ignite Community has released the fourth alpha build of Ignite 3!Ignite 3 is a project that aims to create the next generation of the Apache Ignite platform, modernize and improve the usability of the product while keeping its power and flexibility. It’s been quite a journey since the project started in late 2020 – I’ve been sharing the updates along the way in a series of…
Customer 360 View is a significant aspect of digital transformation, enabling organizations to gain insights into customer behavior. Armed with this understanding, companies can make data-driven decisions to serve their customers with personalized experiences and promote growth through targeted marketing. Yet, gaining this 360 view is data-intensive and requires quick access to up-to-date…